Introducing MobiliseYourCity’s NUMP Guidelines

Global problems, local solutions
Interdependency is now the order to the day. Global problems, such as climate change, cannot be solved by any individual nation and thus require concerted action. On the other hand, consequences are felt, and actions must be implemented, at the local level.
The urban transport sector is no exception. Urban transport is responsible for a major share of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and current projections predict a steep rise of transport emissions in the next decades, a stark contrast to what is needed to achieve the Paris Agreement’s goal of limiting global warming to 2°C. These projections not only stand in line with the expected economic growth (and the consequent increase in energy consumption and mobility needs of citizens), but also with the rapid urbanization rates, especially in developing countries. Simultaneously, mobility significantly affects the quality of lives of citizens. Thus, improving urban transport can not only help mitigate GHG emissions and achieve international agreements and national commitments and goals, but it can improve air quality, reduce health costs, increase productivity, promote equity and make sure that the cities of the future develop in an inclusive and sustainable manner.
The role of national governments
In most countries, planning and development of urban transport is the responsibility of local governments. Nonetheless, many countries all over the world recognize that urban mobility is not merely a local concern; it is of national interest. The complex and interdependent nature of global problems underlines the importance of a robust, coordinated and multi-level policy and investment approach of governments, including a strong role of national governments supporting cities which often lack technical and financial resources to implement sustainable urban mobility measures.
In other words, national governments act as a link by helping solve global problems while exacting transformative change at the local level.
What is a NUMP?
National Urban Mobility Policies and Investment Programs (NUMPs) are strategic, action-oriented frameworks for urban mobility, developed by national governments, enacted to enhance the capacity of cities to plan, finance and implement projects and measures designed to fulfil the mobility needs of people and businesses in cities and their surroundings in a sustainable manner. It builds on existing policies and regulations and aims at harmonizing relevant laws, norms, sector strategies, investment and support programs towards and integrated approach for the benefits of cities and their inhabitants. It takes due consideration of participation and evaluation principles.
By developing and implementing NUMPs, national governments can help tap many different benefits by supporting the transition towards sustainable urban mobility, such as:
- Enabling cities to prosper in a sustainable manner by providing cities with the capacities, resources and orientation they need to address urban mobility challenges.
- Facilitating investment in sustainable urban mobility through the provision of a stable and long-term framework for investment decisions.
- Contributing to achieve national and international policy objectives, such as the nationally determined contributions (NDCs) to the Paris Agreement and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), by involving all levels of government and societal actors and fostering low-carbon and sustainable transport based on the Avoid-Shift-Improve-Fuels approach.
- Securing stakeholder commitment for transforming the urban mobility system by making use of a multi-stakeholder approach that fosters common understanding, creates ownership and secures the contribution of central stakeholders.
- Improving policy coordination both between national ministries and between the local and national levels.
NUMPs can be divided into three different types:
- Policies or sectoral strategies
- Support or investment programmes
- Mix of policy and programme
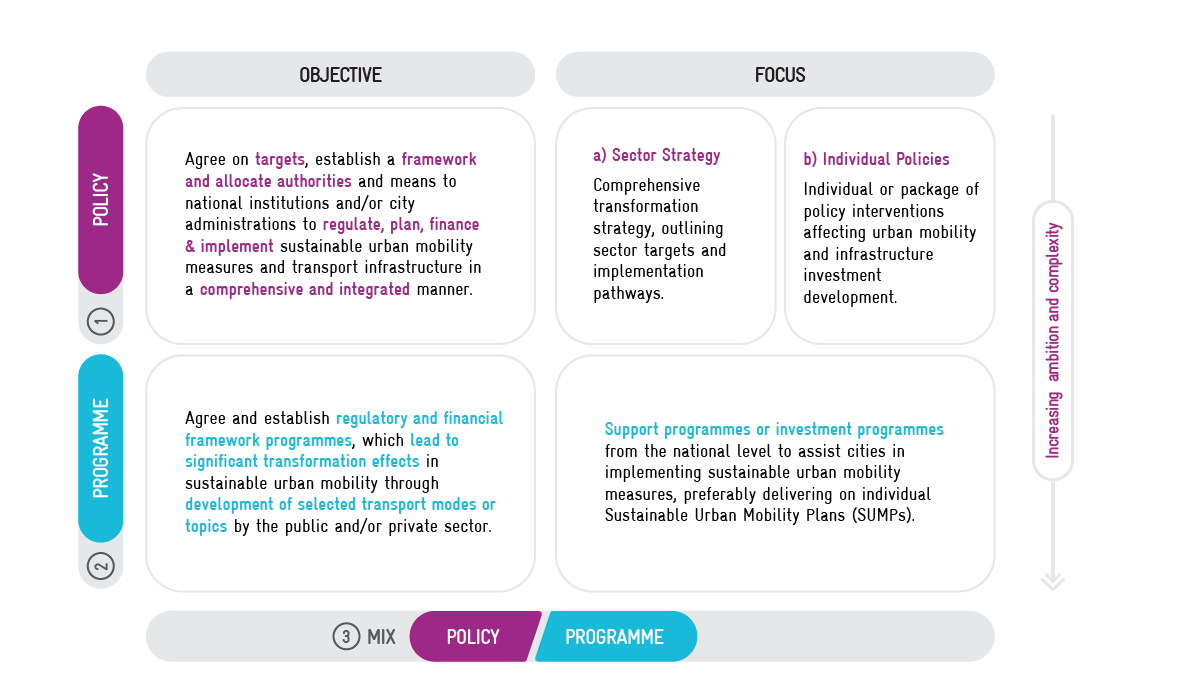
The NUMP Guidelines
The NUMP Guidelines have been developed by the MobiliseYourCity Partnership, in cooperation with the Urban Electric Mobility Initiative (UEMI) and aim to support national governments prepare National Urban Mobility Policies and Investment Programmes (NUMPs). These guidelines have been the result of the Partnership’s vast experience built from working together with national governments all over the world.
The NUMP Guidelines acknowledge that no process is identical, and each NUMP needs to take due consideration of the different national contexts within which they are developed. Nonetheless, the Guidelines provides a hands-down and highly practical approach on how to develop a NUMP following a standardized and widely-tested process: the NUMP Cycle.
The NUMP Cycle consists of 4 Phases and 15 key Steps providing orientation for the NUMP development process. The entire process is likely to require around two years of work, depending on the level of depth of the individual steps and on the type, scope and focus of the NUMP process.
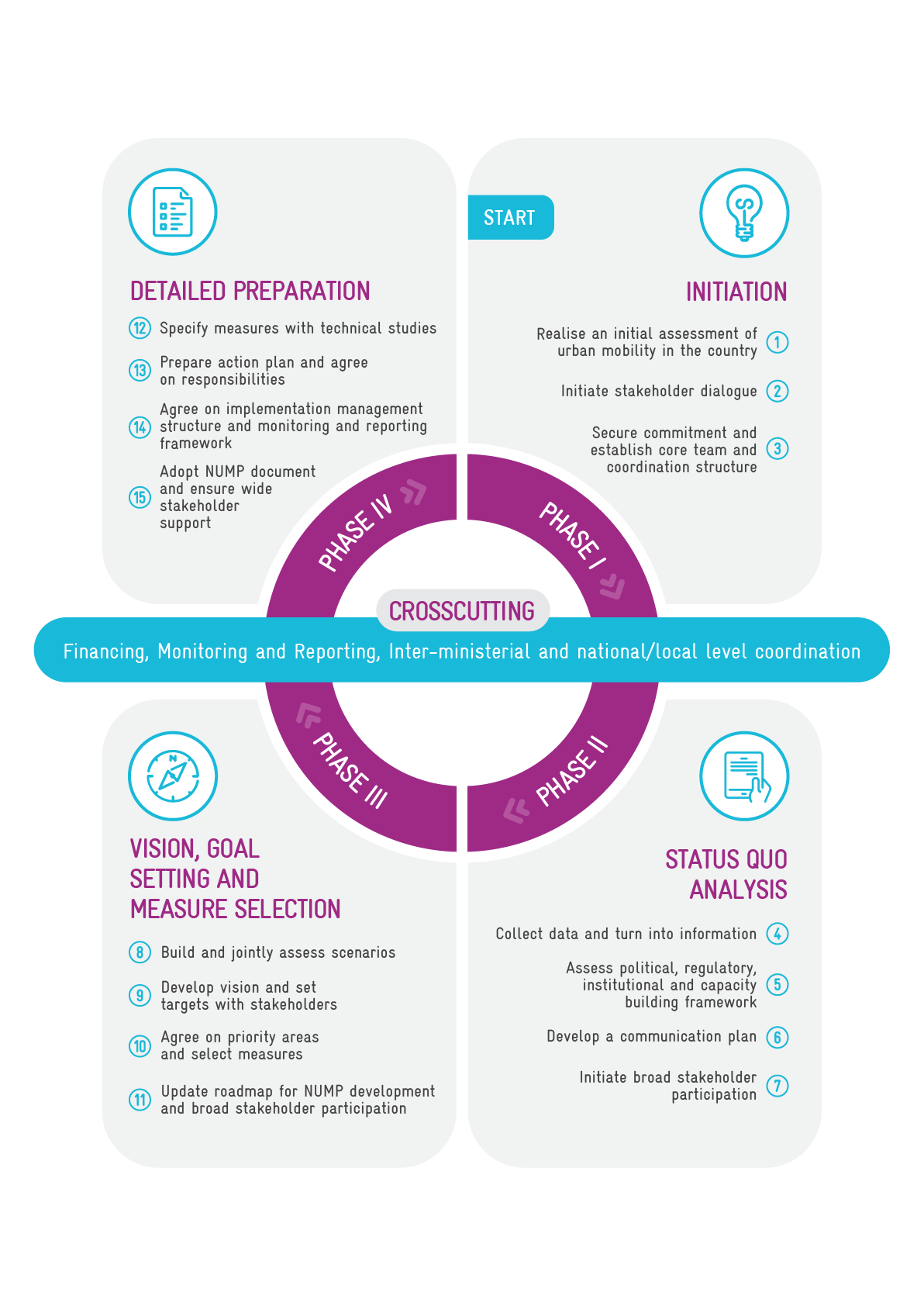
The Guidelines provide a structured and detailed explanation of each Phase and Step, thus facilitating its use: users can easily jump to each Phase and Step, according to their own needs and interests.
If you are interested in learning more about NUMPs and the NUMP Cycle or are in the process of developing a NUMP for your country, download the Guidelines here.
The NUMP Guidelines are part of a comprehensive NUMP toolkit developed by GIZ for national governments and urban mobility practitioners. The Toolkit is structured along the NUMP Cycle and provides valuable tools that can be used in each NUMP Phase.
Access the NUMP Toolkit here and the latest article to learn how it works here.
Many countries have already benefitted from MobiliseYourCity’s approach to developing NUMPs. Here is a list of finished NUMP reports: