Sustainable Urban Mobility Transformation in Antofagasta, Chile: A Model for Progress

Antofagasta, Chile, has undergone a remarkable transformation in its urban mobility system thanks to the implementation of a Sustainable Urban Mobility Plan (SUMP). With an area of 30,718 square kilometres and a population of 388,545, Antofagasta is a bustling regional capital characterised by its strong ties to the copper mining industry. The region's GDP per capita of USD 47,000 demonstrates its economic significance. However, rapid urbanisation and its economic opportunities have presented unique mobility and environmental challenges. As a result, the city has been proactive in adopting sustainable transportation measures.
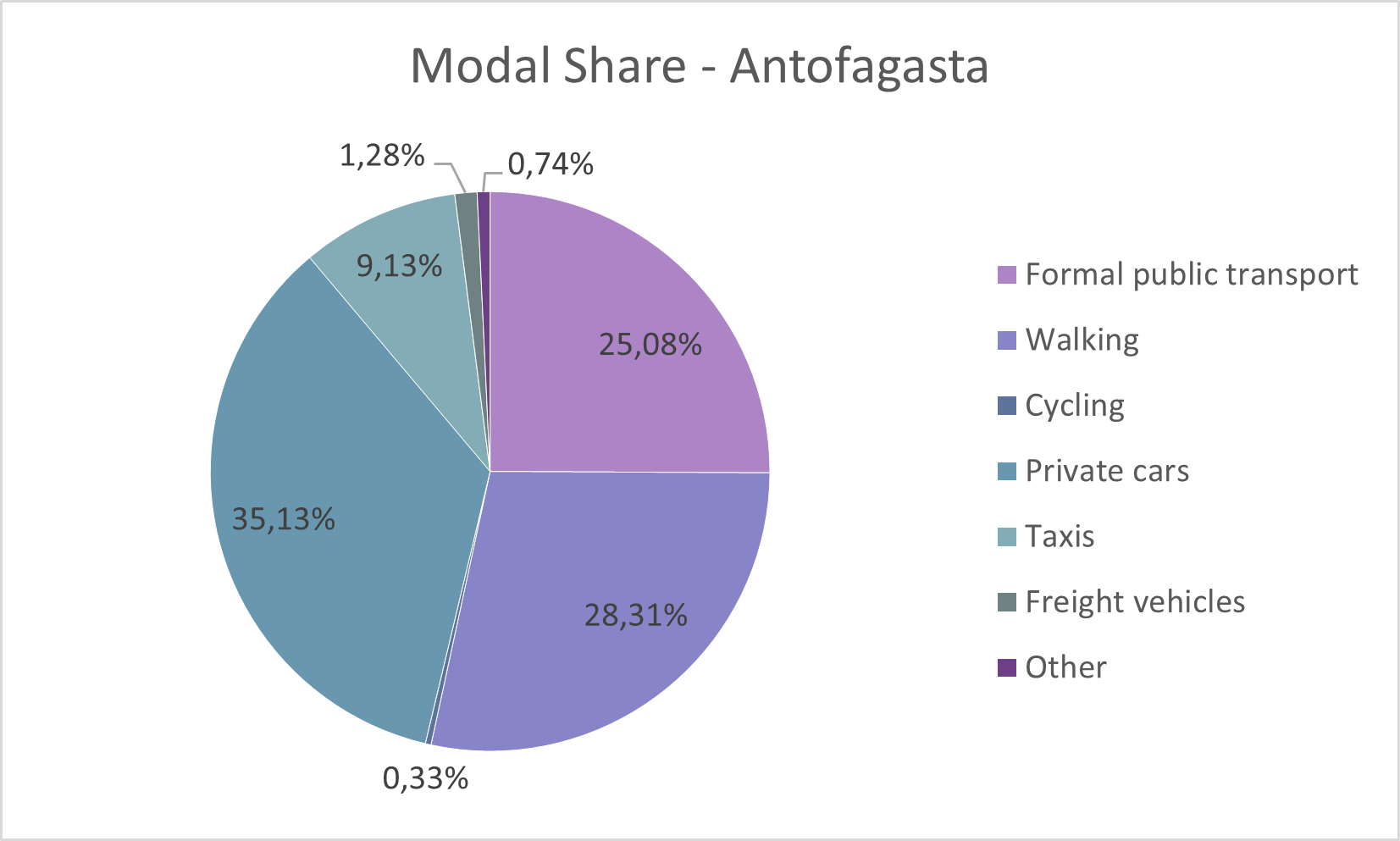
Antofagasta's mobility landscape has evolved significantly, with various modes of transportation contributing to the city's overall modal share. In 2017, the breakdown was as follows:
Antofagasta faced significant challenges in urban mobility.
The city's rapid growth and geographic constraints led to congestion and a strained transport network. The economic activities were predominantly concentrated in the city centre, exacerbating traffic issues. The presence of private trains dividing the city created additional hurdles in terms of traffic flow.
To address these challenges, the Regional Government, in collaboration with local authorities and various institutions, initiated a series of mobility projects. However, the lack of coordination among these initiatives raised questions about their overall impact, especially regarding emissions.
Antofagasta's Drive to Sustainable Mobility with a Comprehensive SUMP
The SUMP, funded by the European Union and implemented by GIZ through the EUROCLIMA+ Programme, has a clear mission. It strives to develop an Integrated Sustainable Urban Mobility Plan incorporating environmental goals and robust monitoring mechanisms. Additionally, the plan seeks to enhance and streamline various modes of transportation within the city. It emphasises the importance of formalising the Technical Board for Sustainable Mobility to provide structure and guidance. Furthermore, the SUMP significantly emphasises training regional and municipal government officials. Lastly, it actively promotes citizen empowerment and engagement in decision-making processes, particularly regarding investment choices.
The SUMP aims to introduce significant changes in Antofagasta's urban mobility landscape. Some of the key measures included in the plan are:
- Renewal of buses and collective taxis fleet.
- Development of a mass transit system.
- Expansion of high-standard pedestrian axes.
- Enhancement of cycle lanes and cycling infrastructure.
- Urban renovation zones and incentives for residential use.
- Traffic calming measures.
- Integration of logistics in land-use planning.
The estimated cost of these measures is USD 1,222,680,555, with the majority allocated for physical infrastructure and mass transit development.
The implementation of the SUMP promises substantial positive outcomes:
- Reduction of GHG emissions by 0.36 Mt CO2eq by 2035.
- A decrease in annual transport-related GHG emissions per capita to 600 kg CO2eq by 2035.
- Enhanced accessibility with a significant increase in the population living near public transport stops.
- A rise in the modal share of public transport, walking, and cycling trips.
- Improved road safety, decreasing traffic fatalities per 100,000 inhabitants.
SUMP Success in Antofagasta: Key Discoveries Revealed
The SUMP implemented in Antofagasta emphasises the need to tailor global methodologies to the local context, recognising that one size does not fit all. It also underscores the pivotal role of public participation in cost-effective and efficient engagement strategies, emphasising the significance of involving the community. Effective communication is vital in gaining public support and raising awareness of the SUMP's objectives. Additionally, collaborative budgeting among various government levels is instrumental in SUMP implementation. Integrating sustainable urban mobility planning with other urban development instruments is crucial, as it considers the unique characteristics of the local context, making it a central aspect of the process.
Moreover, Antofagasta has set an example by establishing Chile's first SUMP mobility observatory, demonstrating the city's commitment to transparency and accountability in implementing sustainable urban mobility measures.
In conclusion, Antofagasta's Sustainable Urban Mobility Plan showcases a model for addressing complex urban mobility and environmental challenges. Through comprehensive planning, public engagement, and a commitment to sustainability, the city is taking significant steps towards a greener, more accessible, and safer urban environment.